Table of Contents
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...
- Declining incidence of chickenpox in the absence of universal childhood ...
- Infographic - Chickenpox - CHICKENPOX people who never had chickenpox ...
- Distribution of chicken pox cases by month over a 4-year surveillance ...
- Deaths from chickenpox | The BMJ
- (PDF) Seasonal and epidemiological profile of chickenpox cases in ...
- Chickenpox cases by district fr | Download Scientific Diagram
- Estimated incidence rates of chickenpox by week, Japan, 2002-2005 ...
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...


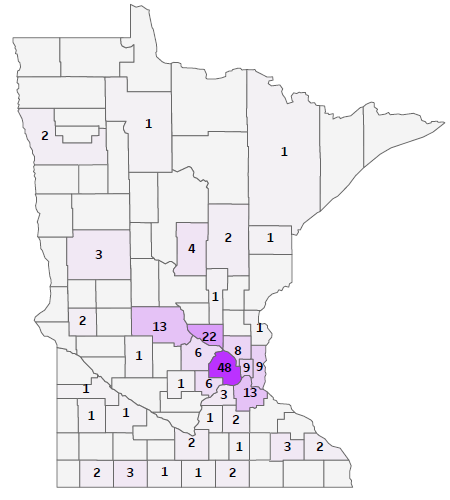
Understanding Rt Values



Current Trends by State

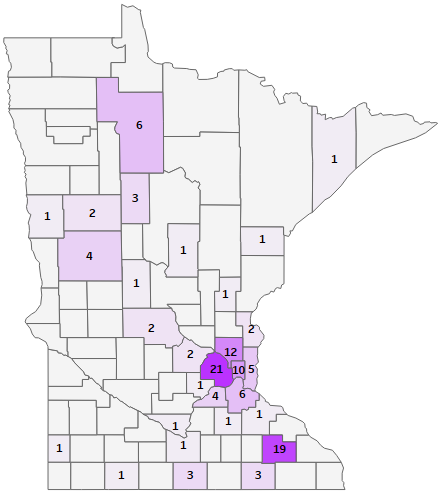
For example, states with low Rt values (Rt < 0.5) are generally seeing a decline in new cases, indicating effective control measures. These states often have robust healthcare systems, high vaccination rates, and strong adherence to preventive measures among their populations. On the other hand, states with high Rt values (Rt > 1.5) are experiencing an increase in new cases, suggesting that current measures may not be sufficient to curb the spread of the disease. These areas may require more stringent public health interventions, increased testing, and enhanced community outreach programs to reduce transmission.


Implications for Public Health Policy
The analysis of Rt values for states has significant implications for public health policy. By closely monitoring these values, policymakers can assess the effectiveness of current strategies and make informed decisions about whether to tighten or relax restrictions. Moreover, understanding the factors that contribute to changes in Rt values can help in tailoring interventions to the specific needs of each community, thereby optimizing resource allocation and improving outcomes. The tracking of current epidemic trends by state based on Rt values is a powerful tool in the fight against infectious diseases. By providing real-time insights into the spread of epidemics, these values can guide public health responses, ensuring that interventions are targeted, effective, and proportionate to the risk. As we move forward, the continued monitoring and analysis of Rt values will remain crucial, not only for navigating the challenges of ongoing epidemics but also for preparing for and responding to future health crises. By working together and leveraging data-driven approaches, we can build resilient communities better equipped to face the complexities of infectious disease management.For the most current and detailed information on Rt values and epidemic trends in your state, it's essential to consult official public health resources and academic research. These sources provide comprehensive data and expert analysis, helping individuals and communities make informed decisions to protect their health and well-being.
